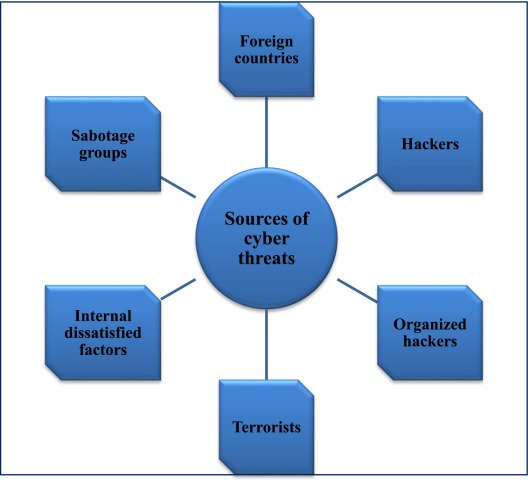
The Current Cybersecurity Landscape
The current cybersecurity landscape is characterized by an alarming increase in both the frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks. As technology continues to advance, cybercriminals are leveraging these innovations to develop more intricate strategies. This evolution in tactics has rendered the traditional defense mechanisms insufficient, necessitating a reevaluation of existing cybersecurity frameworks by both individuals and organizations.
One prevalent type of attack is phishing, which involves deceiving individuals into providing sensitive information, such as passwords or financial details. Phishing attempts often come disguised as legitimate communications from trusted entities, making it crucial for users to develop an acute awareness of potential scams. The evolving tactics within phishing, such as spear phishing and whaling, target specific individuals or high-profile executives, increasing the stakes and potential impact of these attacks.
Ransomware is another significant threat within the current cybersecurity environment. This malicious software encrypts data, rendering it inaccessible to its rightful owners until a ransom is paid. Over recent years, ransomware attacks have grown exponentially, with cybercriminals not only encrypting files but also threatening to leak sensitive information if the ransom is not met. This trend has introduced new layers of complexity for organizations striving to protect their data integrity and reputation.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) further exemplify the sophisticated nature of contemporary cyber threats. These attacks are typically carried out by well-resourced adversaries with specific objectives, often targeting sensitive government or corporate networks over prolonged periods. APTs involve stealthy intrusion techniques, ensuring that the attackers remain undetected while they exfiltrate information or disrupt operations.
In light of these evolving threats, the importance of robust cybersecurity measures has never been more critical. Organizations must prioritize holistic cybersecurity strategies that encompass not just technological fortifications but also education and awareness initiatives to empower individuals against these pervasive risks.
Common Cybersecurity Threats Explained
In today’s digital landscape, organizations and individuals alike face a plethora of cybersecurity threats that can compromise sensitive information and operational integrity. One of the most prevalent threats is malware, a term used to describe malicious software designed to harm, exploit, or gain unauthorized access to systems. Examples of malware include viruses, worms, and ransomware. Recent high-profile ransomware attacks, such as the Colonial Pipeline incident, underscore the devastating impact malware can have on infrastructure and operations.
Another critical threat is social engineering, which involves manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information often through deceptive tactics. Phishing attacks are a common form of social engineering, where attackers impersonate legitimate entities to trick users into providing sensitive data like passwords or financial information. Notable breaches, such as the Target data breach in 2013, began with a targeted phishing campaign that exploited employee trust.
Organizations also face risks from insider threats, where current or former employees with authorized access intentionally or unintentionally expose the organization to risks. Insider threats can range from data theft to accidental disclosures, making them particularly challenging to combat. The case of a former employee at Tesla stealing company secrets highlights the potential damage that can occur from trusted individuals misusing their access.
Additionally, the Dark Web plays a significant role in facilitating various cybercrime activities. This obscure part of the internet provides a marketplace for illegal goods, including stolen data, hacking services, and malware. Cybercriminals often leverage the anonymity that the Dark Web offers to execute their malicious activities while remaining difficult to trace. Understanding these common threats is crucial for individuals and organizations to develop effective cybersecurity strategies that mitigate potential risks.
Impact of Cybersecurity Threats on Businesses and Individuals
The impact of cybersecurity threats on both businesses and individuals has become increasingly profound in recent years. As cyberattacks evolve in sophistication, they pose significant financial, reputational, and operational risks to those targeted. Financially, businesses can suffer devastating losses. According to recent statistics, the average cost of a data breach for a business is approximately $4.35 million, a figure that includes direct costs such as remediation, legal fees, and fines, as well as indirect costs such as lost revenue and decreased customer trust. This financial burden can be detrimental, particularly for small to medium enterprises that may lack the resources to recover.
Reputational damage also emerges as a critical concern. A cybersecurity breach can lead to loss of consumer trust, as customers become wary of engaging with businesses that have compromised their sensitive data. An instance that underscores this risk is the 2017 Equifax data breach, which affected approximately 147 million Americans. The fallout from this event included a significant decline in stock prices and a long-term reputational crisis that the company is still addressing. Businesses must recognize that cybersecurity is not merely an IT issue, but a fundamental aspect of overall business strategy and customer relationship management.
Operationally, cybersecurity threats can disrupt the functionality of organizations. Cyberattacks, such as ransomware attacks, can halt business operations altogether, leading to significant downtimes. For example, the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack in 2021 resulted in severe disruptions to fuel supply on the East Coast of the United States, showcasing how cyber threats can have wide-ranging implications that extend beyond the immediate victim. As such, it is essential for businesses and individuals alike to understand and prioritize cybersecurity to mitigate these escalating threats.
Strategies to Mitigate Cybersecurity Risks
As the landscape of cybersecurity threats continues to evolve, it is imperative for both individuals and organizations to adopt effective strategies to mitigate these risks. A proactive approach to cybersecurity can significantly enhance protection against potential breaches and attacks.
One of the foundational tactics in safeguarding digital assets is the regular updating and patching of software systems. Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software, making timely updates essential. Organizations should establish a schedule for automatic updates across all devices and systems, ensuring that they are equipped with the latest security features. This practice not only minimizes vulnerabilities but also ensures compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Additionally, employee training plays a critical role in enhancing cybersecurity measures. Human error is frequently the weakest link in an organization’s security posture; therefore, implementing regular training sessions can help staff recognize potential threats such as phishing attempts and social engineering tactics. By fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness, companies can significantly reduce their susceptibility to attacks. It is also important to create clear protocols for reporting suspicious activities, which encourages vigilance among employees.
Incident response planning is another crucial element in mitigating cybersecurity risks. Organizations should develop and routinely test an incident response plan to address potential security breaches swiftly and efficiently. This plan should delineate roles and responsibilities, establish communication channels, and outline steps for containment, eradication, recovery, and reporting. Effective incident response can minimize damage, reduce recovery time, and protect sensitive information.
Finally, embracing advanced security technologies is vital for a robust cybersecurity framework. Solutions such as firewalls, encryption, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint protection can provide layers of defense against sophisticated threats. Organizations should assess their specific needs and consider the integration of these technologies to create a comprehensive security architecture.
By implementing these strategies, individuals and organizations can fortify their defenses and significantly mitigate the risks associated with escalating cybersecurity threats.